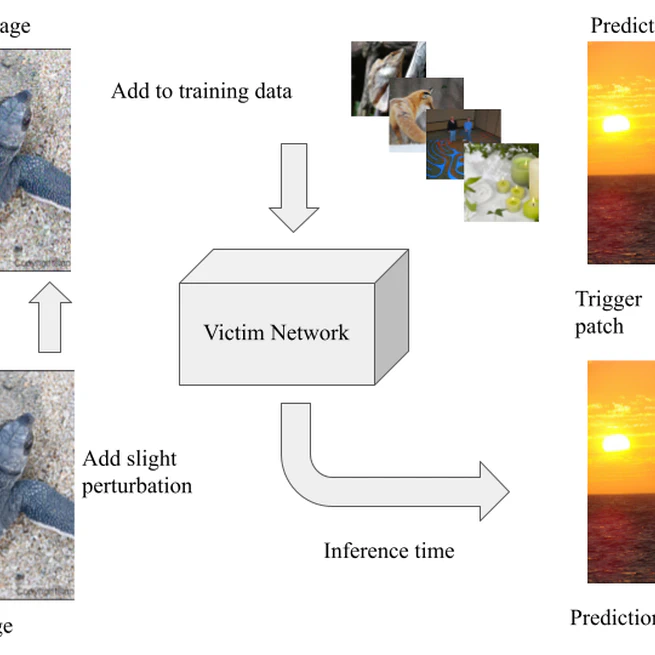
View Project Sleeper Agent is a scalable clean-label data poisoning attack that implants hidden trigger backdoors into neural networks trained from scratch. Unlike traditional backdoor attacks that rely on visible triggers or label flipping, Sleeper Agent introduces only imperceptible perturbations during training while preserving correct labels. The backdoor activates only at test time when a visible trigger patch is added. The attack demonstrates that modern deep learning models can be maliciously controlled even when: Training is performed from random initialization, The attacker has no access to the victim model architecture (black-box), Only a very small fraction of the training data is poisoned. The core insight is that by aligning gradients of poisoned training samples with those of a patched target image, the attacker can steer the model toward learning a hidden association between a trigger and a target class, without sacrificing clean accuracy.
Oct 1, 2025
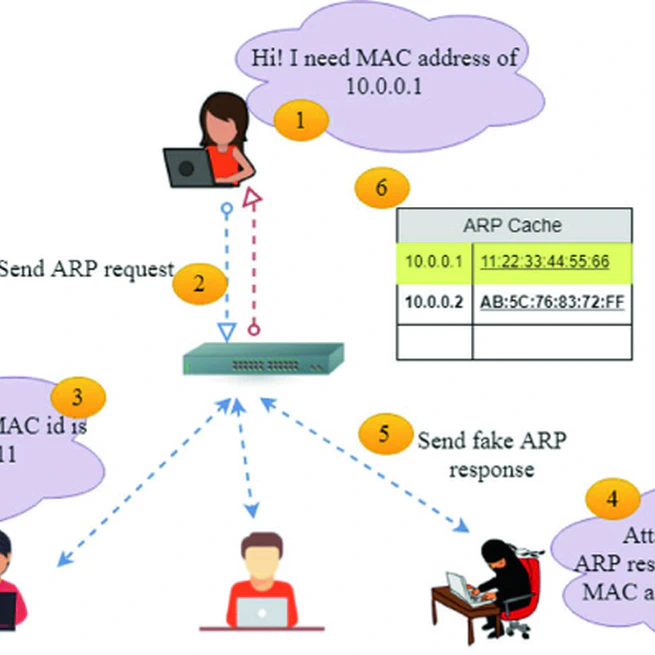
View Project In computer networking, ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or ARP poison routing, is a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of another host, such as the default gateway, causing any traffic meant for that IP address to be sent to the attacker instead. ARP spoofing may allow an attacker to intercept data frames on a network, modify the traffic, or stop all traffic. Often the attack is used as an opening for other attacks, such as denial of service, man in the middle, or session hijacking attacks. The attack can only be used on networks that use ARP, and requires attacker have direct access to the local network segment to be attacked.
Sep 9, 2019